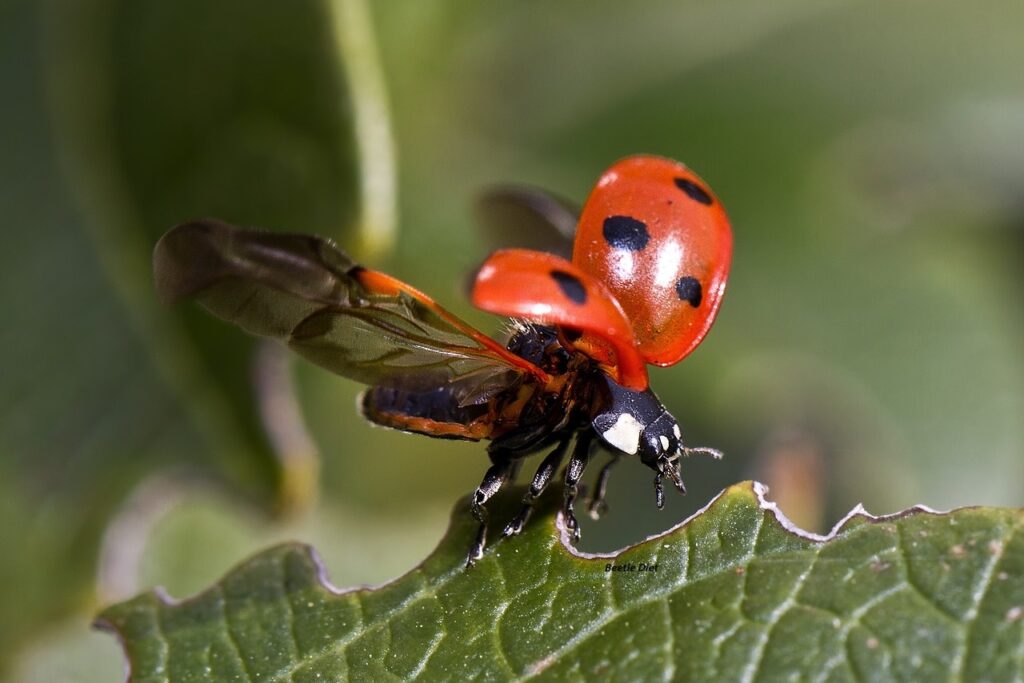
Introduction
The beetle diet is as diverse as the species themselves, encompassing a wide range of foods that support their survival in almost every ecosystem on Earth. Beetles are among the most adaptable creatures, thriving in forests, deserts, aquatic environments, and even urban landscapes. Understanding their dietary habits offers insight into their ecological roles and why they are essential for maintaining natural balance.
Beetles exhibit a wide spectrum of feeding behaviors, from scavenging dead organic matter to preying on other insects or even feeding on fungi and wood. This article explores the fascinating beetle diet, shedding light on what these resilient insects eat and how their choices impact the world around them.
What Do Beetles Eat?
Beetles have evolved to adapt their diet based on the environment they inhabit. Their food preferences can be categorized into four main groups: herbivores, carnivores, detritivores, and omnivores.While their feeding helps plants reproduce, some herbivorous beetles can become agricultural pests, causing significant crop damage.
Understanding the Beetle Diet: What Do Beetles Eat?
Explores the diverse dietary habits of beetles, ranging from plants to fungi, insects, and decaying matter.
Herbivorous Diets in Beetles
Different species of beetles have specialized diets. Herbivorous beetles typically feed on plants, while carnivorous beetles hunt other insects. Some beetles are scavengers, feeding on decomposing organic matter, and others are omnivores. Their diets are influenced by their environment, with food choices affecting their role in the ecosystem
Carnivorous and Scavenging Beetles
Beetles serve multiple roles in the food chain, from being primary consumers of plants and animals to becoming food for predators. Their varied diets make them important contributors to ecosystem dynamics, facilitating processes like pollination, pest control, and decomposition. Their feeding habits help maintain a balance of species and resources in their habitats.
The Role of Beetle Diets in Ecosystem Balance
Highlights how beetle feeding habits contribute to pollination, pest control, decomposition, and nutrient cycling.
Decomposers and Nutrient Cycling
Detritivorous beetles, like dung beetles, break down decaying matter, returning essential nutrients to the soil. This process enriches the earth, promoting plant growth and supporting biodiversity. Beetles aid in recycling organic materials, preventing the buildup of waste and contributing to healthier, more fertile ecosystems.
Pest Control and Pollination
Carnivorous beetles, such as ladybugs, naturally control insect pest populations, keeping plant diseases in check. Herbivorous beetles, while feeding on plants, often inadvertently pollinate flowers, promoting plant reproduction. Through these actions, beetles help ensure the stability of plant and animal populations in their environment.
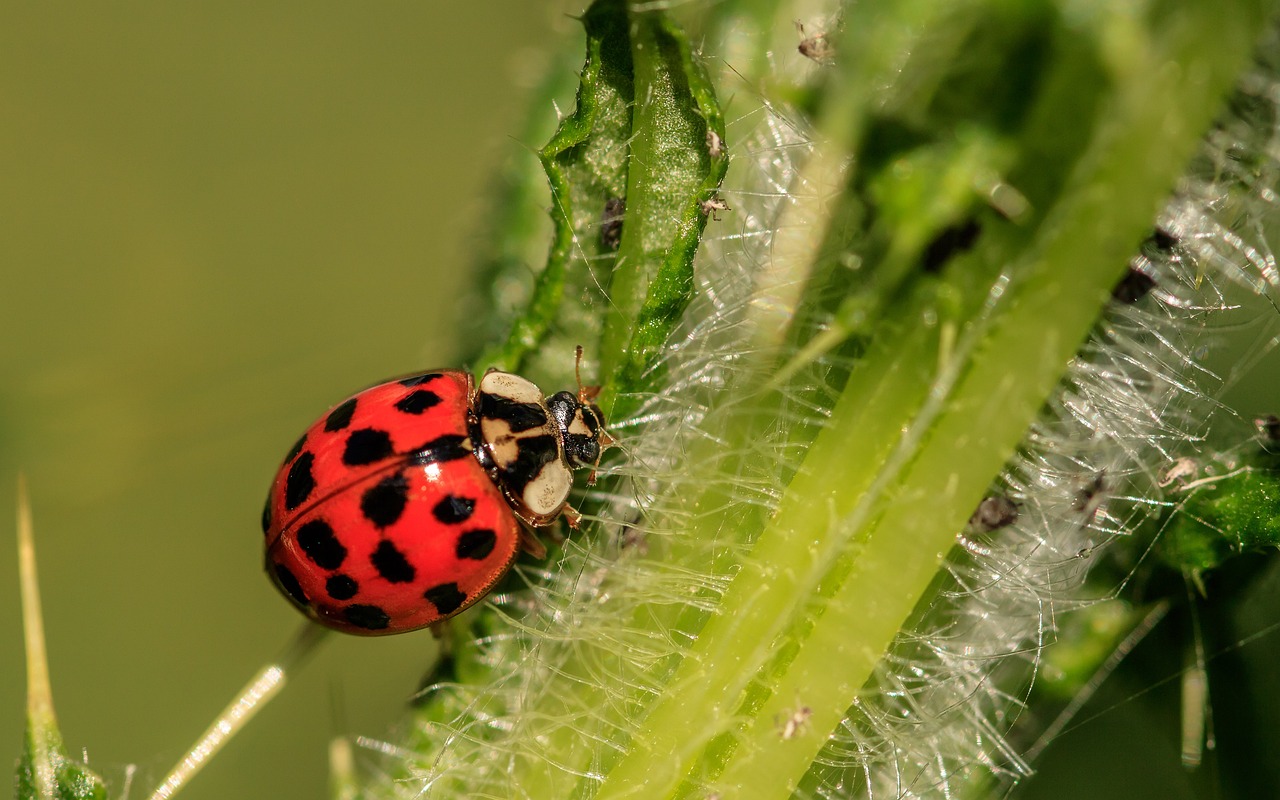

Types of Beetle Diets Herbivores, Carnivores, and More
Breaks down the main categories of beetle diets, showing their adaptability and ecological roles.
Herbivorous Beetles and Plant Consumption
Herbivorous beetles primarily consume plant material such as leaves, stems, and seeds. These beetles can sometimes become agricultural pests, especially when they target crops. However, they also play a positive role in ecosystems by helping plants spread their seeds and pollinate.
Carnivorous Beetles as Natural Predators
Carnivorous beetles prey on other insects, contributing to natural pest control. Species like ground beetles feed on harmful insects, helping reduce crop damage and maintain a balance in the food web. Their presence helps regulate insect populations, keeping harmful pests in check.
Adaptations That Help Beetles Thrive on Their Diet
Examines physical and behavioral traits that allow beetles to access and consume various foods.
Mandibles and Specialized Mouthparts
Beetles possess strong mandibles designed for chewing and breaking down tough plant material, hunting prey, or scavenging. Some species, like wood-boring beetles, have evolved specialized mouthparts for consuming wood or tough organic matter, allowing them to survive in diverse environments.
Enzyme Production and Digestion
Many beetles produce enzymes to help digest complex materials, such as cellulose in wood. This adaptation is particularly seen in wood-boring beetles, which break down wood fibers to extract nutrients. Similarly, beetles that consume fungi or decaying matter often rely on microbial enzymes to aid digestion.
How Human Activities Impact the Beetle Diet
Analyzes how deforestation, pollution, and pesticide use affect beetle feeding patterns and survival.
Effects of Habitat Loss on Beetles
Urbanization, deforestation, and agriculture reduce the availability of food sources for many beetle species. Habitat destruction can lead to a decline in plant and animal populations that beetles rely on, diminishing their food supply. Loss of habitat also limits areas where beetles can find shelter and breed.
Pesticide Use and Pollution
Pesticides used in farming can have harmful effects on beetles, especially those that feed on plants or other insects. The chemicals often reduce beetle populations by directly poisoning them or destroying their food sources. This disrupts ecological processes like pollination and pest control, making ecosystems less resilient.
How does the beetle diet contribute to environmental health?
The beetle diet plays a vital role in pollination, pest control, decomposition, and nutrient recycling, supporting ecosystem stability and biodiversity.
Habitat Destruction and Food Scarcity
Detritivorous beetles like dung beetles and carrion beetles break down organic matter, turning waste into nutrients that enrich the soil. This process improves plant growth, soil fertility, and water retention in ecosystems. Without these decomposers, organic waste would accumulate, disrupting natural cycles.
Pesticides and Chemical Exposure
Carnivorous beetles, such as ladybugs, control harmful insect populations, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Meanwhile, herbivorous beetles inadvertently assist in pollination by feeding on flowers, contributing to plant reproduction and maintaining biodiversity. These roles help sustain healthy ecosystems and food production systems.
What challenges threaten the natural diet of beetles?
Beetles face threats from habitat destruction, pesticide use, and climate change, all of which disrupt their food sources and ecological roles.
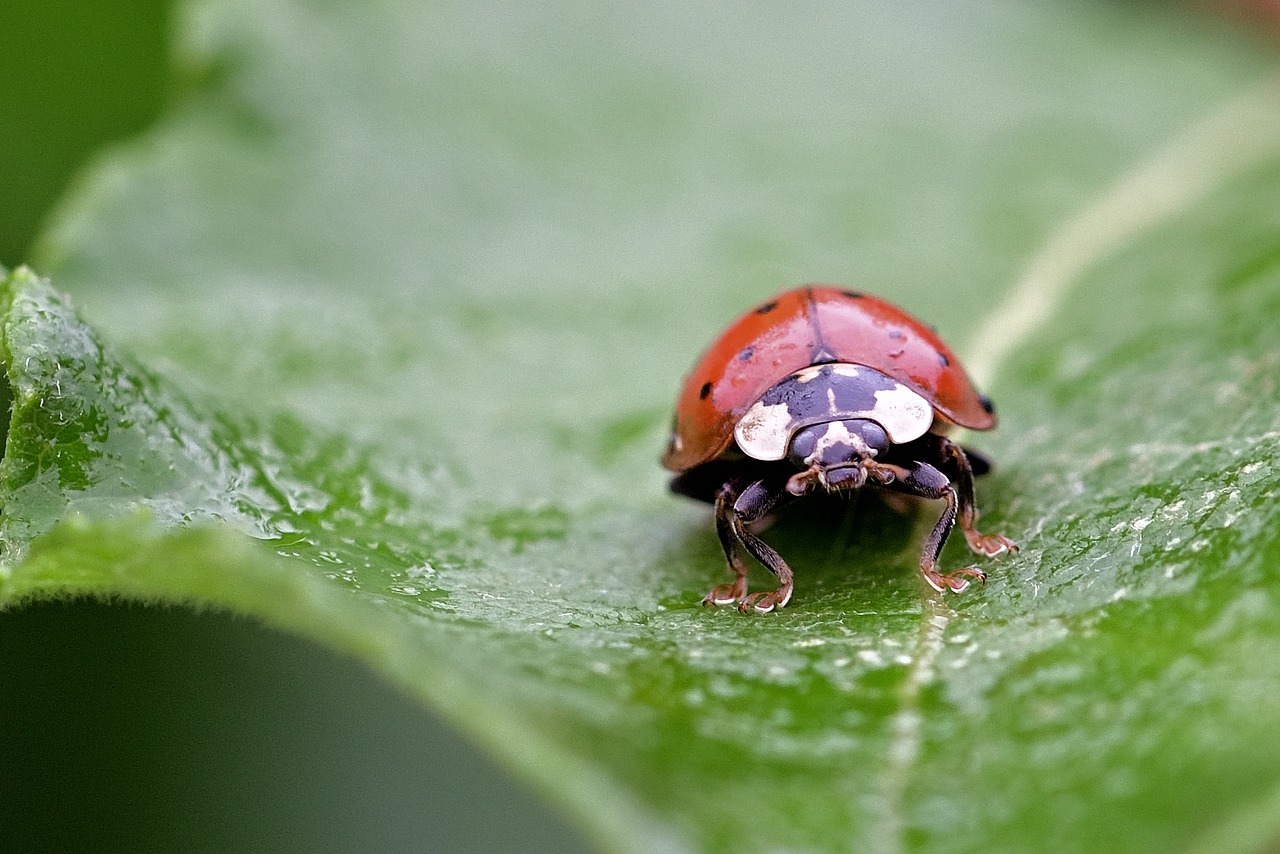

Habitat Loss and Deforestation
Human activities like urbanization and agriculture destroy natural habitats, removing plants and organic materials that beetles rely on for food. For example, herbivorous beetles lose feeding grounds when forests are cleared, while decomposers face scarcity of decaying matter.
Pesticide Use and Environmental Pollution
Pesticides kill beetles directly or harm their food sources, disrupting their ecological roles. Pollutants in water and soil further degrade the quality of their habitats, making it harder for beetles to access safe and sufficient food. These factors reduce beetle populations, affecting ecosystems globally.
Conclusion
The beetle diet is a cornerstone of ecological stability, influencing pollination, pest control, decomposition, and biodiversity. By understanding their dietary habits, we can appreciate their ecological importance and take steps to protect these remarkable insects. Whether herbivorous, carnivorous, detritivorous, or omnivorous, beetles continue to shape the natural world in extraordinary ways.